Systems and System Components in healthcare
To improve quality in the health care system one must view all services as a series of processes that make up the health system. Inefficiencies in providing health services is directly related to the efficiency of its processes; therefore it is essential for all involved in health service delivery to understand the processes they are part of and how those processes make up the system. Then we can narrow quality gaps and improve services.
A system is a set of interacting and interdependent parts and processes. A system can also be defined as sum of all elements that work together to produce a common goal or product.
Systems are arrangements of organizations; people, materials and procedures associated with a particular function or output. Systems can be small or large, simple or complex.
 |
| Image courtesy |
Examples of systems
A health care facility or hospital is composed of the reception, outpatient, inpatient, CTC, pharmacy, laboratory departments, etc. Each of those are a smaller system comprised of many processes.
There are different systems in human body. The human body is a system that is made up of complex organs and processes. The health care delivery system can be compared to human body, for it is a system made up of complex parts and processes.
Components of a system
A system is made up of the following components
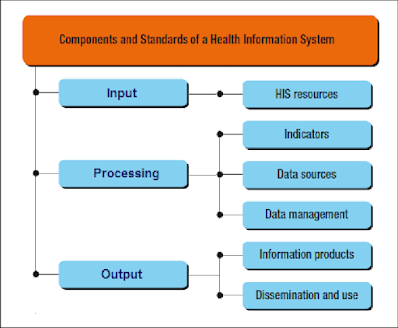
Inputs: Resources required to carry out certain activity, e.g. National health policy, health sector strategic plan, national guidelines, SOPs for clinical and non-clinical services, human resources, time, financial resources, equipment and supply, effective, committed and transparent leadership, team work, infrastructure.
Processes/Activities: series of actions needed to perform a task or transform inputs into outputs, e.g. HRH training, care delivery, implementation of QI approaches in an integrated manner
Output: The immediate results of a process or activity. Product or services resulting from input and processes, e.g. number of health providers trained, supply inventory complete.
There are various relationship between components of a system
- Inputs are the resources required to implement any activity, for example, trainers, content expert, training space and funding
- Activities are what you do with those resources, such as design and develop training materials, plan training sessions, and implement training.
- Output could be a finalized training package and a number of trained professionals.
- Outcomes are when the trained professionals use their training to benefit their facilities and clients.
- Impact refers to the long-term outcome, such as optimally-running facilities and improved health of the community.
Importance of systems and processes
As health care system strive to join the ranks of other high-reliability organizations, many health settings continue to struggle with the basic challenge of developing reliable systems. Reliable systems can reduce defects and rework and facilities safer care of our patients, thereby improving patient outcomes. They can also improve respect for people’s work and increase the joy in their work, and enable patients to know when variations in care occur.
Process
A process is a series of activities needed to perform a task or transform inputs into outputs. Health services delivery involves a number of processes occurring simultaneously, each affects the quality of service offered. In order for a process to be carried out well, the following must be clearly defines:
- What needs to be done
- Why it needs to be done
- How it should be done
- Who should do it
- When should it be done
Importance of processes
In most situations processes are at the root of quality problems (not people). In order to improve quality, we must be able to understand thoroughly the processes involved in the service delivery system. Processes may need to be modified to improve the quality of the system.
The majority of quality problems are in poorly designed processes or systems. Improvement of the system will depend on the extent to which we are able to understand, analyse and re-design processes.
Difference between system and processes
There is a distinct difference between systems and processes
- A process produces results through the completion of one activity where as a system produces results through the interaction of multiple units
- Processes produce outputs whereas systems produce outcomes or impacts
- Process owners manage activities to produce required outputs whereas system managers manage interactions to produce desired outcomes.
Process Analysis for Health system Reliability
Reliable health systems depends on efficient and effective processes
Process analysis refers to gaining a deeper understanding of potential problems in a process by conducting a series of steps designed to identify areas for improvement to improve quality of service delivery.
Process analysis answers the question, “HOW?’’
There are two kinds of process analysis
- Directional (or perspective) process analysis asks: how do you do it? For example, how to conduct a blood test or how to sign patients in at a clinic
- Informational (or descriptive) process analysis asks: how does the process work? For example, how does the blood test work or how does the process of medical records and patient documentation work?
Importance of process analysis
Inefficiency in a process results in time wastage, unnecessary steps and extra work to a system, ultimately reducing quality of service. Process analysis makes it possible:
- To identify problems and understand underlying causes
- To provide a clear framework for identifying parts of the process that require change
- To enable teams to communicate what they are doing and why
KEYWORDS
- components of health care system
- 6 components of health system
- six building blocks of health system
- six building blocks of health system
- examples of healthcare systems
- what are the building blocks of health system
LINKS
- https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/258734/9789241564052-eng.pdf
- https://www.capacityproject.org/framework/other-health-system-components/
- https://www.physio-pedia.com/Health_Care_Systems
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22878/
- https://study.com/learn/lesson/health-care-delivery-system-concept-components-types.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Health_system
- https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2012/04/20061215DCortese.pdf
.jpeg)
%20injection.png)



0 Comments